堆
堆(Heap)是计算机科学中一类特殊的数据结构的统称。堆通常是一个可以被看做一棵树的数组对象。堆总是满足下列性质:
- 堆中每个节点的值都大于等于(或者小于等于)其左右子节点的值
- 堆总是一棵
完全二叉树
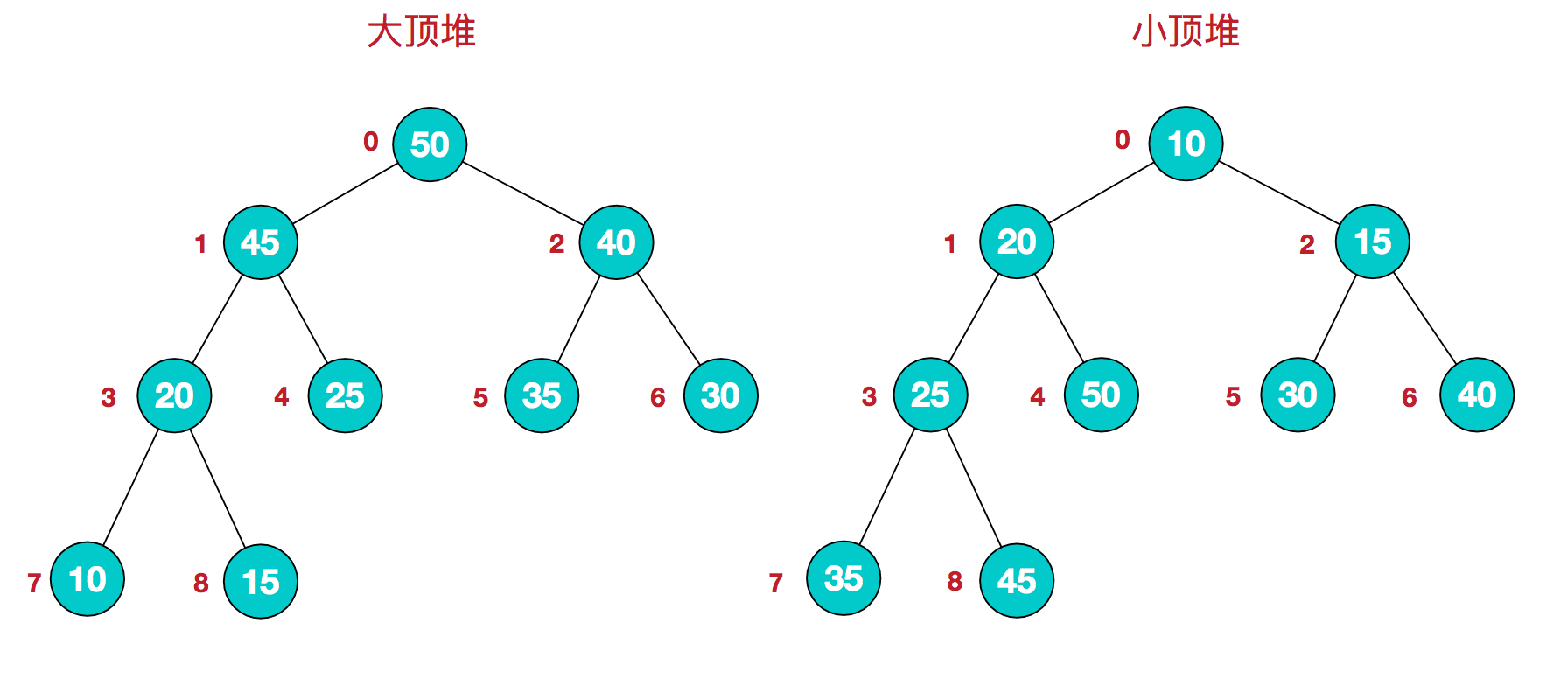
二叉堆
二叉堆是一颗完全二叉树,二叉堆分为大顶堆(最大堆)和小顶堆(最小堆)。对于每个节点的值都大于等于子树中每个节点值的堆,我们叫作 大顶堆。对于每个节点的值都小于等于子树中每个节点值的堆,我们叫作 小顶堆。
性质:
- 任何一个非树根节点的父节点为
Math.floor((index - 1) / 2) - 任何一个非叶子节点的左子节点为
index * 2 + 1 - 任何一个非叶子节点的右子节点为
index * 2 + 2
堆的实现
要实现堆,我们要先知道,堆都支持哪些操作以及如何存储一个堆:
- 上浮 heapifyUp
- 下沉 heapifyDown
- 插入 Insert
- 弹出
- 取顶 ExtractMax
- 堆排序
在堆的实现时,需要注意:
- 因为是数组,所以父子节点的关系就不需要特殊的结构去维护了,索引之间通过计算就可以得到,省掉了很多麻烦。如果是链表结构,就会复杂很多
- 完全二叉树要求叶子节点从左往右填满,才能开始填充下一层,这就保证了不需要对数组整体进行大片的移动。这也是随机存储结构(数组)的短板:删除一个元素之后,整体往前移是比较费时的。这个特性页导致堆在删除元素的时候,要把最后一个叶子节点补充到树根节点的缘由
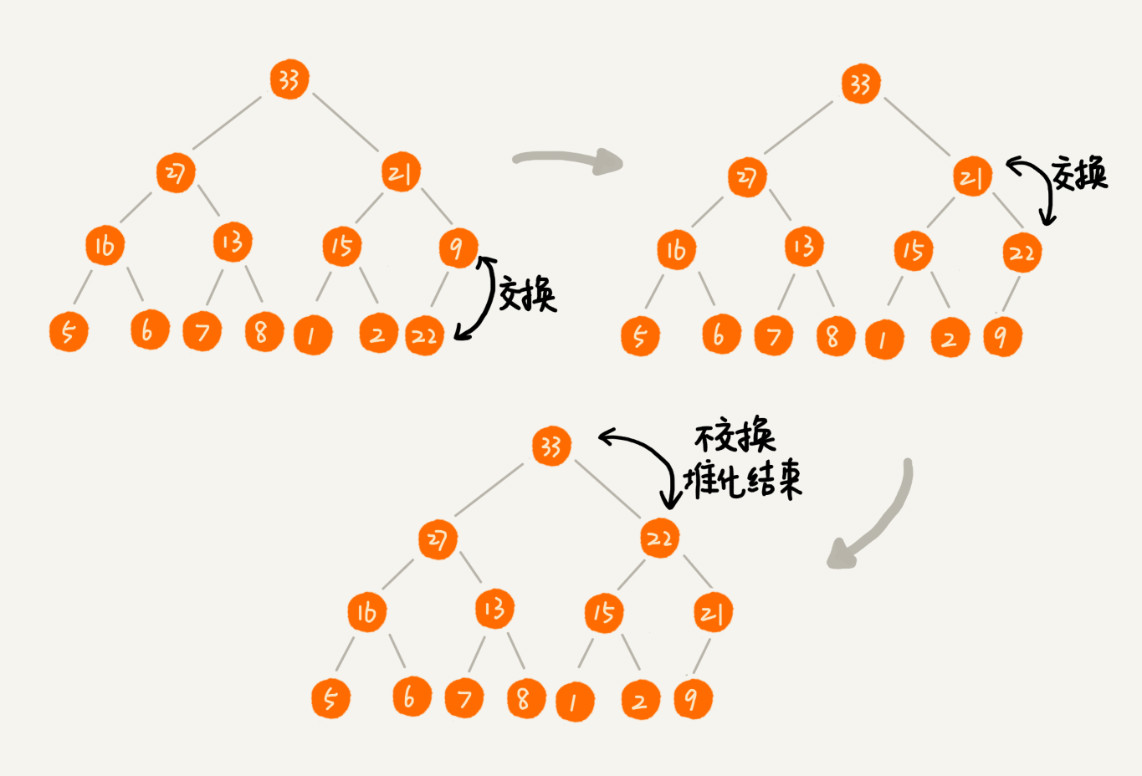
堆化
把新插入的元素放到堆的最后,然后检测是否满足堆的性质。如果不满足则需要进行调整,这个过程称为 堆化(Heapify)。
堆化实际上有两种,从下往上和从上往下。
堆化非常简单,就是顺着节点所在的路径,向上或者向下,对比,然后交换。
代码实现
这里我们以实现最大堆为例:
// 堆元素索引从 1 开始,初始化时先将第一个元素赋值为 0// 堆有 n 个元素,则它的第一个叶子节点是第 n/2 + 1 个,最后一个非叶子节点是第 n/2 个// 将 n 个元素逐个插入到一个空堆中,算法复杂度为 O(n log n)function MaxHeap(arr = []) {this.data = [...arr];// heapify 方式创建堆结构// 利用堆的第 n/2 个元素是最后一个有子节点的元素// 从最后一个有子节点的元素开始向上对每个节点进行堆重构for (let i = this.parent(arr.length - 1); i >= 0; i--) {this.heapifyDown(i);}}MaxHeap.prototype.size = function() {return this.data.length;};MaxHeap.prototype.isEmpty = function() {return !this.data.length;};MaxHeap.prototype.parent = function(index) {if (index === 0) {throw new Error(`index-0 does't not have parent`);}return Math.floor((this.data.length - 1) / 2);};MaxHeap.prototype.leftChildIndex = function(index) {return index * 2 + 1;};MaxHeap.prototype.rightChildIndex = function(index) {return index * 2 + 2;};// 向堆中插入一个元素:插入到最后一个位置,堆插入的元素向上进行堆重构MaxHeap.prototype.insert = function(value) {this.data.push(value);// 将最后一个元素进行上浮操作this.heapifyUp(this.data.length - 1);};MaxHeap.prototype.findMax = function() {if (this.size() === 0) {throw new Error('Heap is empty');}// 大顶堆第一个元素就是最大的值return this.data[0];};// 删除堆中的最大元素:将最后一个元素放到第一的位置,向下进行堆重构Heap.prototype.extractMax = function() {const maxValue = this.findMax();// 堆首尾元素交换this.swap(0, this.data.length - 1);// 删除已经位于堆尾的最大值元素this.data.pop();// 向下堆重构this.heapifyDown(0);return maxValue;};// 向上堆重构:新元素与父元素比较,新元素大则交换,知道新元素比父元素小为止Heap.prototype.heapifyUp = function(index) {while (index > 0 && this.data[this.parent(index)] < this.data[index]) {// 交换数组中位置this.swap(index, this.parent(index));// 是不是依然不满足堆的性质index = this.parent(index);}};// 向下堆重构:从堆顶开始,比较当前元素和两个子元素,将若当前元素小于子元素中的一个,则将当前元素与较大的子元素交换,知道当前元素大于其子元素Heap.prototype.heapifyDown = function(index) {while (this.leftChildIndex(index) < this.data.length) {let leftChildIndex = this.leftChildIndex(index);// 极端情况:当左子节点索引小于数组长度时代表绝对没有右子节点,是叶子节点if (leftChildIndex + 1 < this.data.length &&this.data[leftChildIndex + 1] > this.data[leftChildIndex]) {leftChildIndex = this.rightChildIndex(index);}if (this.data[index] > this.data[leftChildIndex]) {// 满足堆的性质直接挑出break;} else {// 否则继续交换this.swap(index, leftChildIndex);index = leftChildIndex;}}};// 堆数组位置交换Heap.prototype.swap = function(i, j) {if (i < 0 || i >= this.data.length || j < 0 || j >= this.data.length) {throw new Error('Index is out of range');}return ([this.data[i], this.data[j]] = [this.data[j], this.data[i]]);};
我们知道,一个包含 n 个节点的完全二叉树,树的高度不会超过 log2n。堆化的过程是顺着节点所在路径比较交换的,所以堆化的时间复杂度跟树的高度成正比,也就是 O(logn)。插入数据和删除堆顶元素的主要逻辑就是堆化,所以,往堆中插入一个元素和删除堆顶元素的时间复杂度都是 O(logn)。
堆的应用
- 二项堆(Binomial Heap)
- 斐波那契堆(Fibonacci Heap)
- 配对堆(Pairing Heap)
- 左偏树/堆(Leftist Heap)
参考资料: